Sustainability Management in Environmental Dimension
Recognizing the global environmental situation and the impact of our operations on all stakeholders, from internal and external factors, the Group is committed to mitigating potential environmental and community consequences. To ensure responsible practices, TTA has established a comprehensive Environmental Policy aligned with the sustainable development goals. This policy aims to manage environmental risks and opportunities associated with business operations across key areas, including energy efficiency, water management, greenhouse gas emissions and climate change management, and waste management. Additionally, TTA regularly reviews its Environmental Policy to ensure its relevance and effectiveness in addressing evolving circumstances and emerging sustainability issues. Any amendments to the policy or changes in material sustainability matters require approval from the Sustainable Development Committee (SDC) and, subsequently, by the Board of Directors.
Environmental Policy
TTA prioritizes responsible business operations and environmental sustainability. TTA integrates environmental management into its business practices to enhance operational efficiency and drive sustainable growth. The detailed Environmental Policy is publicly available on the Company’s website: (https://www.thoresen.com/storage/download/corporate-documents/20220520-tta-environmental-policy-en.pdf)
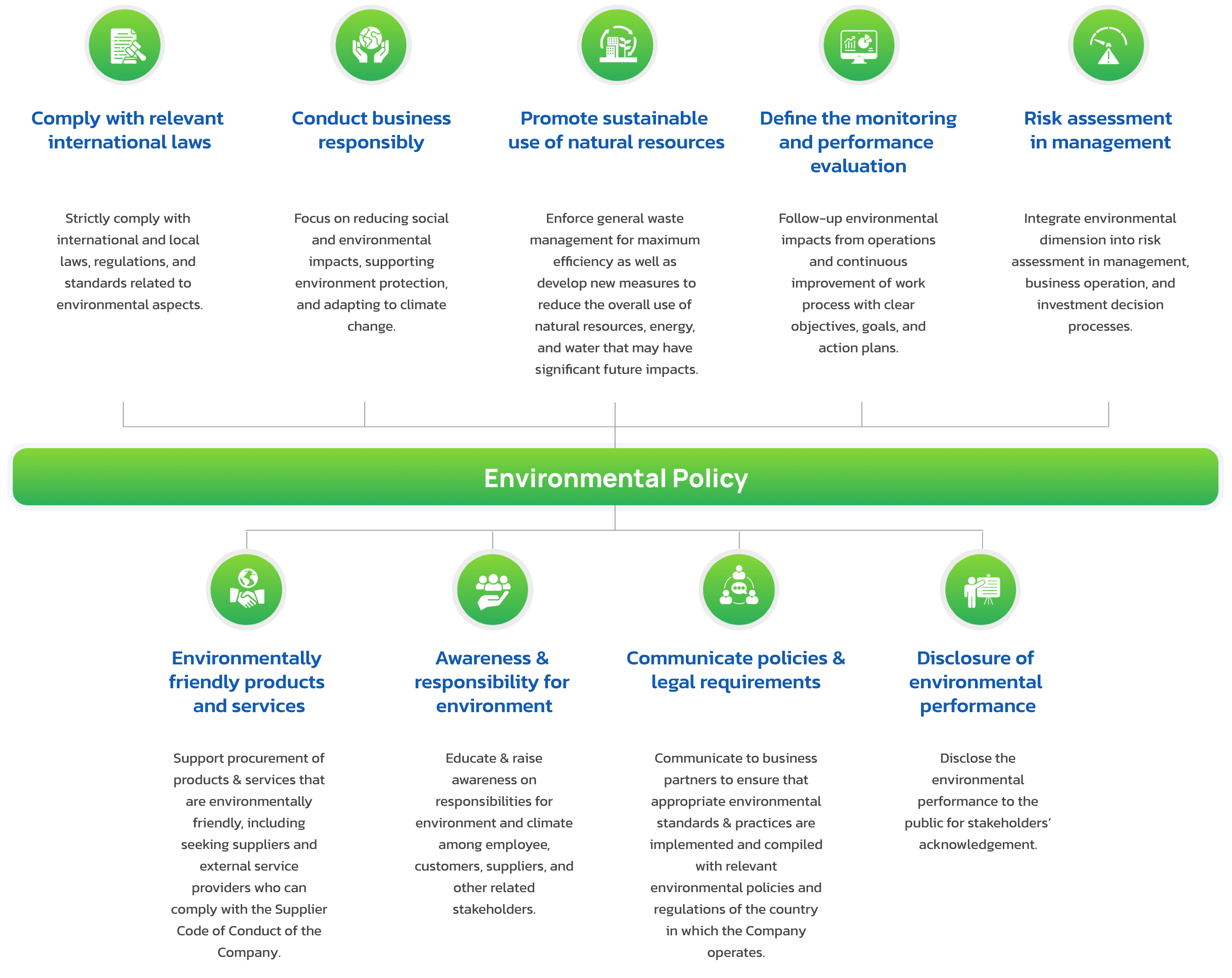
The Group complies with all relevant environmental regulations and standards. TTA conducted an online training on Environmental Policy communication for employees on 13 January 2025, to enhance awareness and compliance. The participation was 71.43 percent, and the average post-training test score was 91.16 percent. The policy is prominently displayed on TTA’s portal, internal bulletin boards, and website.
-
Energy Efficiency
-
Energy Efficiency(3-3)
Amidst global challenges such as continuous population growth and economic expansion, increasing resource and energy demand has heightened the importance of effective energy management. This trend coincides with rising global temperatures, emphasizing the urgency of sustainable solutions. As Thailand is a signatory to the Paris Agreement under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), committed to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, the Group acknowledges the complexities of energy management and the critical importance of conserving limited energy resources. Effective energy management is therefore an urgent priority and a key factor in sustaining business operations.
Energy efficiency plays a crucial role in reducing production costs and mitigating environmental impacts. TTA integrates sustainable resource and energy consumption practices into its Environmental Policy, and assigns the Administrative Department to oversee energy management within its headquarters. Furthermore, TTA continuously strives to explore renewable energy opportunities to advance its transition toward clean and environmentally friendly energy solutions. These efforts align with TTA's Environmental Policy and reinforce its commitment to sustainable business operations.
Energy Efficiency Management Approach and Performance(302-1)
Thoresen Thai Agencies: TTA
Energy Efficiency Management Approach
Efficient energy management is critical to business operations, as energy represents a significant cost factor in driving industries and production processes. Furthermore, energy consumption contributes to climate change through greenhouse gas emissions, a pressing global concern. In response, TTA has set a target to reduce electricity consumption by 2 percent compared to the previous year. This initiative aligns with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG 7) and aims to minimize the environmental impact of energy use and greenhouse gas emissions.
Energy Management Activities and Initiatives
Energy Conservation Initiatives
In 2024, TTA developed and implemented energy conservation initiatives to continuously promote electricity reduction. Key actions included encouraging employees to unplug devices or switch off equipment when not in use, implementing preventive maintenance plans for air conditioning systems and electrical appliances to ensure optimal efficiency, replacing 4 outdated air conditioning units with energy-efficient models representing 17 percent of the total units to reduce environmental impact, and optimizing workspace allocation to maximize energy efficiency while maintaining a suitable and compliant working environment. These efforts reflect TTA’s commitment to sustainable energy management, ensuring compliance with best practices and relevant regulations.
Performance
While TTA implemented several energy-saving initiatives, the organization's overall electricity consumption increased in 2024. Total electricity usage was 819,099 kWh, an 11.2 percent increase compared to 2023, thus not achieving the 2 percent reduction target. However, due to the Metropolitan Electricity Authority (MEA) increased electricity rates, which significantly impacted TTA because its electricity costs are managed through a property management for its commercial building. This resulted in an 18.4 percent increase in the electricity bill. Additionally, TTA expand its operational space in 2024 as part of the Company restructuring to accommodate a broader range of businesses and a growing number of employees. When adjusted for this 20 percent expansion in operational area, the 18.4 percent increase in electricity costs aligns closely with the increased space usage.
2022 2023 2024 Fuel and Energy Consumption of TTA Electricity Cost (Baht) 3,719,529 4,842,129 5,733,693 ↑ 18.4 percent Electricity Consumption (kWh) 826,587 736,344 819,099 ↑ 11.2 percent Electricity Consumption per Unit of Revenue (kWh per Baht) 0.131 0.204 0.381 ↑ 86.8 percent Diesel Fuel Consumption (liters) 3,682 3,586 4,677.53 ↑ 30.4 percent Gasoline Consumption (liters) 9,599 13,794 16,650.36 ↑ 20.7 percent Total Energy Consumption within the Organization (kWh) 947,784.18 893,255.79 1,012,033.59 ↑ 13.4 percent Thoresen Shipping: TSS
Energy Efficiency Management Approach
The company is committed to aligning its operations with environmental policies, recognizing the critical importance of efficient energy use and strict adherence to relevant regulations and standards. To support this commitment, the company has established the Marine Operations and Technical Team, responsible for providing technical support and overseeing all operations related to environmental management.
To ensure that fleet operations meet international standards and comply with the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, Annex VI (MARPOL Annex VI), the company has implemented policies and strategies to optimize fuel consumption across the fleet. This includes collecting data on fuel usage and CO2 emissions.
Thoresen Shipping's cargo vessels have adopted the Alpha Lubricator system to control the consumption of lubricating oil in the main engine cylinders. Additionally, speed-boosting devices have been installed on the propeller shafts to improve vessel performance, enabling ships to travel faster while maintaining the same engine speed, thus reducing fuel consumption and conserving energy. Furthermore, an Onboard Management Manual for Engine Power Limitation (EPL) has been developed to promote energy saving and has been certified by the Shipowners' Association.
Energy Management Activities and Initiatives
Thoresen Shipping implemented hull coating improvements to enhance propulsion efficiency. The company also effectively managed fuel consumption for its fleet operations. Data collected in 2024 from the company's 24 vessels revealed the use of approximately 99,753 tons of high-sulfur fuel oil (HSFO), comprising 6,013 tons of low-sulfur fuel oil (LSFO) and 93,740 tons of very-low sulfur fuel oil (VLSFO). The fleet also consumed approximately 9,857 tons of diesel fuel.
Other Energy Conservation Projects
- Propeller Grit Paint: The application of grit paint on the propeller helps reduce fuel consumption by approximately 2 percent.
- Propeller ECO-Cap: Replacing the propeller blade attachment with ECO-Cap technology helps reduce fuel consumption by approximately 2 percent.
Performance
2022 2023 2024 Fuel and Energy Consumption of TSS Diesel (liters)
6,264 5,302 9,857 ↑ 85.9 percent Fuel Oil (liters)
102,892 91,847 99,753 ↑ 8.60 percent PH Capital: PHC
Energy Management Approach
The company operates restaurants under the "Pizza Hut" brand and recognizes that electricity consumption represents a significant operating cost, from production processes to product delivery and distribution. To reduce electricity and fuel consumption (both of which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions), and to meet the company's goal of reducing electricity usage by 2 percent compared to 2023, a policy was established to decrease electricity consumption per branch by 5 percent compared to 2023 across all 196 branches. The Operations and Technical Training & Development departments are responsible for planning, setting branch-specific targets, and training employees on the proper use and maintenance of electrical equipment. Furthermore, measures to control and reduce daily electricity consumption are implemented at every branch, with each location required to record daily consumption on a company form and ensure usage aligns with set targets. Moreover, the company monitors and plans for effective energy and equipment management, continuously analyzing instances of abnormal electricity consumption to identify causes and implement corrective actions.
Energy Management Activities and Initiatives
Electricity Usage Reduction Project across 196 Branches
The company controls the use and maintenance of electrical equipment and implements measures to reduce daily electricity consumption across all branches. An employee manual guides the efficient use, maintenance, and operation of electrical appliances in the restaurants, including proper procedures for switching equipment on and off. Training sessions reinforce understanding, and external companies are contracted for regular preventive maintenance of electrical equipment, such as air conditioning systems and refrigeration units. Monthly reports, utilizing an online Daily Usage Tracker form, track and measure each branch's performance.
In 2024, the company's overall electricity consumption increased by 3.3 percent. This was attributed to extended operating hours designed to accommodate more customers during nighttime, particularly those working late or ordering late-night meals at branches in tourist areas. However, the Energy Management Committee successfully reduced electricity costs per unit during 2024, resulting in a savings of Baht 4.19 million (a 2.7 percent reduction) from 2023. Despite this cost reduction, the company did not meet its target of reducing overall electricity consumption by 5 percent.
For 2025, the company will focus on further reducing electricity consumption at each branch. Additional operational plans are being developed, including procuring energy-efficient equipment, downsizing refrigeration units, and minimizing the number of unused electrical devices. These measures are designed to enhance operational efficiency and achieve the established energy-saving goals in the future.
Solar Rooftop Project
To promote clean energy use, reduce dependency on traditional energy sources, and support the organization's sustainability goals, the company initiated the Solar Rooftop project. The project commenced with the installation of solar power systems in the first 4 branches in August 2024, with a total investment of Baht 910,000 . The initial implementation of the Solar Rooftop system in these branches demonstrated an average reduction in electricity consumption of approximately 3,400 kWh per month, resulting in average electricity cost savings of 8.41 percent per branch compared to regular electricity expenses. This highlights the effectiveness of clean energy and its potential to reduce energy costs. Furthermore, the project contributes to increasing clean energy use and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with the company's environmental and long-term sustainability goals. The company plans to expand the installation of the Solar Rooftop system to additional branches in the future, further enhancing energy savings and generating a more significant positive environmental impact.

Performance
Remark: The company does not use fuel in its operations.2022 2023 2024 Fuel and Energy Consumption of PHC Electricity Cost (Baht)
136,476,523 155,931,973 151,737,850 ↓ 2.7 percent หน่วยไฟฟ้า (กิโลวัตต์-ชั่วโมง)
26,566,090 26,985,875 27,874,578 ↑ 3.3 percent ผลรวมการใช้พลังงานภายในองค์กร
95,637 97,949 100,348 ↑ 2.4 percent Mermaid Maritime: MML
MML is certified to ISO 14001:2015.
The ISO 14001:2015 standard for internal environmental management, which will be applied to MML's workplaces in 2024, will allow the company to better evaluate and mitigate the environmental effects of its operations. The following channel allows you to examine the specifics of the approved workplaces: https://www.mermaid-group.com/storage/document/accreditation/20240312-accreditation.pdf
Energy Consumption
MML's Scope 2 emissions for 2024, derived from purchased electricity and renewable energy generation, demonstrate the company’s progress toward reducing its carbon footprint. The data aligns with GRI 305-2a standards and reflects a proactive approach to energy efficiency and sustainability. The 2024 performance highlights the integration of renewable energy into operations, achieving significant reductions in emission intensity
Key Performance Indicators
Purchased Electricity in 2024: The total purchased electricity was 634,890 kWh, a decrease from 932,952 kWh in 2023. This decline reflects energy-saving initiatives and increased reliance on renewable energy sources. Carbon emissions from purchased electricity were reduced to 267 tCO2 equivalent, compared to 417 tCO2 equivalent in 2023.
Renewable Energy Generation: MML expanded its renewable energy generation (Solar Rooftop) to 243,543 kWh in 2024, significantly up from 81,840 kWh in 2023. This addition contributed to offsetting 93 tCO2 equivalent.
Total eCO2 Emissions: Total Scope 2 emissions were reduced to 360 tons in 2024, down from 450 tons in 2023, achieving a net decrease of 20 percent.
Initiatives and Strategies in 2024
Energy Efficiency Measures: Improved energy-efficient systems were implemented in office facilities, including compartmentalized air conditioning and energy-efficient chillers. These systems significantly reduced electricity usage without compromising operational efficiency. Efforts to optimize energy use included tracking real-time electricity consumption, enabling timely interventions and energy-saving measures.
Renewable Energy Integration MML has significantly increased its use of renewable energy through the installation of solar panels on some of its buildings, enabling the production of clean energy and reducing reliance on non-renewable electricity sources.
Greenhouse Gas Scope 2 (305-2a) 2022 2023 2024 Target Purchased Electricity (kWh)
611,646 932,952 634,890 eCO2 intensity = 0.6 (5 percentage reduction) eCO2 (tons)
283 417 267 Renewable Energy Generation (Solar Rooftop) (kWh)
- 81,840 243,543 eCO2 (tons)
- 33 93 Total eCO2 (tons)
283 450 360 Annual Revenue (US$ 000,000)
224 274 513 eCO2 Intensity (tons/US$)
1.3 1.6 0.7 Solar Rooftop: Pinthong Building Surroundings Project
The company has implemented a sustainable energy initiative at its Pinthong facilities by installing LED solar-powered lightings system around the building premises. This project underscores the company’s commitment to reducing electricity consumption and environmental impact and achieving cost efficiency.
Project Details
Lighting Specifications:
- 34 units of 100W LED solar-powered lights were installed across 3 buildings:
- Building A 13 units
- Building B 14 units
- Building C 7 units
- Total installation cost: Baht 77,350 plus Baht 10,000 for installation services
Energy and Cost Efficiency
Energy Consumption:
- Each light operates for 12 hours daily (6:00 PM to 6:00 AM)
- The total daily electricity consumption is calculated as: (100 W × 34 units / 1,000) × 12 hours = 40.8 units / day
- Monthly consumption: 1,224 units/month
- Annual consumption: Approximately 14,688 units/year
Cost Savings:
- Monthly electricity savings: Baht 4,244.7
- Annual electricity cost savings: Baht 50,936.4
Future Commitments
MML aims to achieve a 5 percent reduction in eCO2 intensity by 2025, further reinforcing its commitment to sustainability and net zero.
PM Thoresen Asia Holdings: PMTA
Energy Efficiency Management Approach
PMTA invests in Baconco Co., Ltd., a company specialising in agricultural chemicals. Baconco primarily develops, manufactures, and distributes agricultural chemical products in Vietnam and other countries. Its product portfolio includes NPK compound fertilisers, single fertilisers, composite fertilisers, and foliar fertilisers. Additionally, they sell pesticides and insecticides in Vietnam. These manufacturing processes may cause negative environmental impacts due to high consumption of various types of energy. Therefore, PMTA implements energy management practices by conducting periodic energy audits to monitor, inspect, and evaluate the company's energy usage throughout each operational year.
Furthermore, PMTA has established measures to reduce energy consumption, such as requiring proper maintenance of electrical equipment and machinery to ensure appropriate and efficient operation, campaigning to turn off all electrical equipment when not in use, and setting workplace air conditioning temperature to no lower than 25 degrees Celsius. These are the main measures in the company's energy management strategy.
Unique Mining Services: UMS
The company recognizes and prioritizes environmental issues that may arise from its business operations by establishing environmental management policies, as well as promoting and educating employees at all levels in the organization to be aware of and strictly comply with the following:- Develop and improve the factory and production processes to minimize environmental impact by implementing systematic prevention methods
- Expand business into renewable or other clean energy sources, such as solar power and biomass energy
- Regularly conduct activities to contribute to society, community, and environment, to improve the quality of life in communities where the company is located, both through independent initiatives and in cooperation with government authorities and local communities
- Take responsibility and remain committed to environmental protection as well as preserving local customs and traditions in areas where factories are located
- Prevent accidents and control waste emissions to remain below acceptable standards
- Respond quickly and effectively to incidents that affect the environment and community resulting from the company's operations, by cooperating with government officials and relevant agencies
Solar Rooftop Project
In 2024, the company was able to generate 5.81 GWh of electricity from solar roofs, which reduced CO2 emissions from electricity generation by 1,999 tCO2 equivalent or reduced coal usage from electricity generation by 810 tons, which is equivalent to planting 109,153 trees.
Asia Infrastructure Management (Thailand) : AIM
In 2024, due to the limited space of the office, the company can produce electricity from solar rooftop for office use at the amount of 6 kilowatts/month and can reduce electricity costs by approximately 15-20 percent per month. In the future, AIM, as a business operator of installing solar power generation systems, plans to expand the solar power generation system installation project to other subsidiaries.
-
Water Management
-
Water Management(3-3)
The growing demand for water has intensified shortages across various sectors, as water remains a crucial resource for industries, ecosystems, and biodiversity. Many regions, both domestically and internationally, continue to face challenges such as water scarcity, declining water quality, excessive consumption, and increasingly stringent wastewater discharge regulations. Recognizing these issues, the Group prioritizes effective water management, particularly within its operations.
The Group strictly adheres to relevant laws and regulations, ensuring efficient water management aligned with its Environmental Policy. It promotes wastewater treatment and reuse in production processes, thereby reducing raw water costs, wastewater discharge volume, and treatment expenses. These measures help mitigate water pollution risks, support business continuity, and minimize community concerns. Furthermore, the Group is committed to ensuring that affiliates comply with environmental policies through clouse monitoring and risk assessment.
Water Management Policy
The Group has established a water management policy as an integral part of its broader Environmental Policy, emphasizing the sustainable use of natural resources. The ISO 14001:2015 environmental management system is implemented to enhance operational efficiency and service delivery while ensuring compliance with customer requirements, legal frameworks, and relevant regulations. The policy is effectively communicated within the organization to ensure adherence and is disclosed to stakeholders as appropriate.
Thoresen Thai Agencies: TTA
Water Management Approach
TTA has designated the Administrative Department and Human Resources Department as the team responsible for general water management, including recording water usage and identifying irregular consumption patterns for prompt corrective action. The building management team oversees wastewater treatment and discharge, with external agencies conducting regular inspections to ensure water quality improvements. All water used by TTA is supplied by external agencies, specifically the Metropolitan Waterworks Authority. TTA headquarters, located in Orakarn Building on Chidlom Road, is not in a water-stressed area and is under the jurisdiction of the building's management. Consequently, implementing water reduction initiatives such as water recycling, reuse, or pre-discharge treatment is restricted. Nevertheless, TTA recognizes the importance of water recycling and wastewater treatment and remains committed to advocating for these practices within the building.
In 2024, TTA set a target to reduce water consumption at its headquarters by at least 2 percent compared to the previous year. Preventive maintenance plans, including leakage inspections of water fixtures, have been established, alongside awareness campaigns promoting water conservation. All wastewater from TTA is directed to the building's centralized treatment system, where it is treated to meet regulatory standards before being discharged into public waterways, ensuring no untreated wastewater is released.
Water Management Activities and Initiatives
Preventive Maintenance and Leakage Inspection Program
TTA has implemented a scheduled preventive maintenance program to assess the overall condition and operational efficiency of water-related equipment within its offices. This initiative aims to prevent water leakage, minimize unnecessary water wastage, and ensure uninterrupted operations. Any malfunctioning or inefficient equipment is promptly repaired or replaced. The officer of Administrative Department and Human Resources Department are responsible for overseeing this initiative.
Water Conservation Awareness Campaign
TTA has launched a water conservation awareness campaign to promote responsible water usage among employees. Posters and various communication channels are utilized to reinforce key water-saving practices. Additionally, annual refresher training sessions incorporate water conservation topics, followed by knowledge assessments to ensure employee understanding and adherence to best practices.
Performance
Despite these initiatives, total water consumption for 2024 amounted to 2,331 cubic meters, a 26.5 percent increase from 2023. Consequently, TTA did not meet its target of a 2 percent reduction in water usage. This was primarily attributed to workplace expansion and corporate restructuring, leading to investments in a more diverse range of businesses and an increased number of employees. When adjusted for the 20 percent expansion in office space, this aligns with the increasing water expense of Baht 9,780.
2022 2023 2024 Water Management Volume from TTA Operations Water Expense (Baht)
43,020 36,840 46,620 ↑ 26.5 percent Unit (cubic meters)
2,151 1,842 2,331 ↑ 26.5 percent Water Consumption per Revenue Unit (cubic meters/Baht)
0.000342 0.00051 0.00108 ↑ 111.76 percent Units 2022 2023 2024 Total Volume of Water Withdrawal Across All Areas Water from External Agencies
Clean Water (TDS ≤1,000 mg/L) 2,151 1,842 2,331 ↑ 26.5 percent Other Water (TDS >1,000 mg/L) 0 0 0 Consistent Remark : Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) is a measure of the dissolved combined content of all solid, inorganic, and organic substances present in water.Units 2022 2023 2024 Total Volume of Water Withdrawal from Water-Stressed Areas Water from External Agencies Clean Water (TDS ≤1,000 mg/L) 0 0 0 Consistent Other Water (TDS >1,000 mg/L) 0 0 0 Consistent Total Water Consumption in All Water-Stressed Areas 0 0 0 Consistent Thoresen Shipping: TSS
Water Management Approach
Thoresen Shipping prioritizes minimizing marine pollution from its operations to ensure efficient and sustainable maritime transportation. To achieve this, the company strictly adheres to international regulations and continuously sets operational targets for optimal onboard water management.
For freshwater management on vessels, the company strictly complies with international regulations to maximize efficiency. In addition to sourcing freshwater from public utilities at destination ports or purchasing it from local suppliers, vessels are equipped with freshwater generators that convert seawater into potable water. This process involves heating seawater under vacuum to produce steam, which then condenses into freshwater. The generated freshwater is stored in dedicated tanks and undergoes ultraviolet (UV) sterilization and filtration before use in daily onboard activities.
Water Management Activities and Initiatives
Maintenance Plan, Inspection, and Troubleshooting of Ballast Water Treatment (BWT) Systems
The company has successfully installed Ballast Water Treatment (BWT) systems across all 24 vessels in its fleet. These high-quality, internationally certified systems ensure the efficient management of ballast water, effectively preventing the spread of invasive alien species between regions. Consequently, Thoresen Shipping's ballast water discharge does not negatively impact the environment, ecosystems, or biodiversity.
In addition, the company has established a comprehensive maintenance and inspection plan, aligned with the annual servicing schedule, to ensure all BWT equipment operates in compliance with the standards set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and other relevant regulatory bodies. This ensures optimal system performance and environmental compliance.
Furthermore, the company does not source water from water-scarce areas or utilize groundwater in its operations.
PH Capital: PHC
Water Management Approach
Effective water management is crucial to business operations, given government laws requiring wastewater quality control before discharge into public drainage systems. Non-compliance with these standards can result in business disruptions, potential store closures, and fines, leading to increased operational costs. Recognizing the significance of water management, the company has established guidelines for managing water usage, wastewater, and discharge. These include regular grease removal from grease traps, detailed recording of water consumption at each branch to monitor discharge quality, and the implementation of measures to reduce water usage efficiently. Compliance with these policies is mandatory across all branches. Furthermore, the Sales and Operations Departments are designated as the responsible entities for overseeing water management initiatives.
Water Management Activities and Initiatives
Installation of Water-Saving Fixtures and Equipment
The company mandates the installation of water-saving fixtures and equipment, such as foot-operated faucets and air bubble faucets. Additionally, a maintenance team (Handyman) is available to assist with the repair and maintenance of these fixtures as needed.
Grease Removal from Store Grease Traps
All company branches treat wastewater before it is discharged into public areas by installing grease traps to prevent grease from contaminating the water system. Store employees are responsible for skimming grease from the water's surface and disposing of it separately, while non-grease water flows into the shared drainage system of the shopping malls where the stores operate.
Wastewater Quality Inspection and Treatment Before Discharge
External public health agencies regularly and randomly conduct water quality inspections at various branches. Additionally, every 3 months, municipal agencies are contracted to pump out grease residue from the traps. As part of the company's store inspection standards, all branches must conduct an annual water quality analysis to test for coliform bacteria and E. coli, including chemical assessments to ensure compliance with legal requirements. Wastewater or discharge must be treated according to proper sanitation standards before being discharged.
To reinforce effective water and wastewater management, the company provides training for branch employees. Before store openings, employees receive instruction on proper water usage, common grease trap issues, prohibited actions, and cleaning procedures as part of the company's standardized curriculum.
Performance
2023 2024 Water Management Volume from PHC Operations Water Expense (Baht)
2,839,620 2,820,250 ↓ 0.68 percent Unit (cubic meters)
97,038 97,077 ↑ 0.04 percent Remark : Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) is a measure of the dissolved combined content of all solid, inorganic, and organic substances present in water.Units 2023 2024 Total Water Withdrawal Across All Areas Water from External Agencies
Clean Water (TDS ≤ 1,000 mg/L)
97,038 97,077 ↓ 0.1 percent Other Water (TDS > 1,000 mg/L)
0 0 Consistent Total Volume of Water Withdrawal from Water-Stressed Areas Water from External Agencies
Clean Water (TDS ≤ 1,000 mg/L)
0 0 Consistent Other Water (TDS > 1,000 mg/L)
0 0 Consistent Total Water Consumption in All Water-Stressed Areas
0 0 Consistent PM Thoresen Asia Holdings: PMTA
Water Management Approach
For PMTA, the focus is on wastewater management, which is handled by licensed external contractors who manage wastewater generated from business operations. However, the company also manages water usage by implementing measures to ensure efficient water use according to purpose, requiring water valves to be locked or closed when not in use, maintaining and replacing equipment and pipes found to be leaking, and efficiently controlling daily water usage in each department. PMTA records daily water meter readings used in production processes and evaluates water consumption to ensure it meets daily targets. This promotes more efficient water management in production processes, helps reduce unnecessary water usage, and leads to reduced water costs. Additionally, PMTA has installed wastewater treatment systems and regularly conducts inspections, monitors, and reports on waste and wastewater management to government authorities.
PMTA controls water usage by employees and business partners, monitors and fixes water leaks in pipes, records water meter readings categorized by type of production use each day, evaluates daily water consumption to ensure compliance with set standards, and requires email notifications to be sent to relevant departments or production units if water usage exceeds specified limits or targets.
Performance
2022 2023 2024 Water Consumption
35,836 36,074 37,094 ↓ 2.80 percent Treated Wastewater (cubic meters)
6,294 10,354 10,151 ↓ 1.96 percent Asia Infrastructure Management: AIM
Water Management Approach
For the water resource management business, AIM is considered a comprehensive water management and public utility company. The main services of the company are reducing non-revenue water for the Provincial Waterworks Authority and Metropolitan Waterworks Authority. In addition, the company has expanded its business to industrial wastewater treatment and river and canal management. AIM is committed to continuously and sustainably growing its business and contributing to society and the environment throughout its business operations. This includes environmental management through 2 perspectives: water and wastewater management. The details are as follows:
- Innovation in biotechnology for industrial wastewater treatment in collaboration with the Industrial Estate Authority of Thailand.
- The project aims to improve the efficiency of water production and reduce non-revenue water by utilizing advanced technologies that require less space and energy. This will be achieved through collaboration with the Metropolitan Waterworks Authority and Provincial Waterworks Authority to create a mobile drinking water production system.
- Improve the capacity to treat polluted canals for increased cleanliness and decreased accumulation of disease-causing pathogens
-
GHG Emissions and Climate Change Strategy
-
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change Strategy (3-3)
Global climate change remains a critical issue that continues to attract worldwide attention, manifested in increasingly erratic seasonal changes, heatwaves, prolonged droughts, and flooding. Thailand is among the countries that have joined the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and ratified the Kyoto Protocol, as well as participated in the Paris Agreement. Under these agreements, member parties have committed to global cooperation to achieve collective goals in managing and controlling greenhouse gas emissions.
In 2023, Thailand participated in the Conference of the Parties 28 (COP28) conference held in the United Arab Emirates, which emphasized the goals of the Glasgow Climate Pact, focusing on measures to reduce coal usage and phase out inefficient fossil fuel subsidies. The conference also aimed to meet the temperature goal set by the Paris Agreement: limiting global temperature rise to below 2 degrees Celsius compared to pre-industrial levels (circa A.D. 1900) and striving to limit it to 1.5 degrees Celsius. The agreement also addressed the establishment of a financial fund by a group of major polluting countries to compensate for "Loss and Damage," aimed at helping vulnerable countries impacted by the climate crisis.
Thailand has set its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) in 3 sectors: 1) Energy and Transportation, 2) Waste Management, and 3) Industrial Processes and Product Use. The country aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 20-25 percent by 2030. The Group is committed to being part of a responsible business community that mitigate climate change. TTA has established a comprehensive Environmental Policy that includes responsible business operations, resource efficiency, and promotion of climate adaptation throughout its supply chain. This is to fulfill the country’s goal and its own goal of becoming Asia’s leading investment company with sustainable growth both in terms of business and social and environmental responsibility.
Climate Change Risks to the Business Operations of the Group
Type of Risks Risks and Opportunities Forecasted Impact on the Group Financial Risks Long-term Climate change risks contribute to natural disasters such as floods and droughts. Operational disruptions may lead to delays in project delivery, penalties, damage claims for contractual breaches, and revenue shortfalls compared to projections. Strategic Risks Long-term Risks arising from technological changes may impact the organization’s ability to adapt, along with challenges posed by consumer expectations for environmentally friendly products, which require adoption of new technologies for effective management. Costs associated with technological upgrades, as well as modifications to products and services that rely on new technologies, may result in increased operational expenses. Regulatory Risks Long-term Regulatory and legal risks stem from evolving government policies and legislation related to climate change, such as the draft Climate Change Act and the Energy 4.0 policy, which aims to promote clean energy by 2036. Adjustments to business plans to ensure compliance with evolving regulations and legal requirements may necessitate higher-than-anticipated investments in certain projects. Operational Risks Long-term Acute physical impacts of climate change, such as flooding, transportation disruptions, and difficulties in employee commuting, etc. Employee absenteeism due to travel disruptions can delay operations, result in workforce shortages, and potentially lead to business interruptions. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change Management Approach of the Group
The Group places great importance on maximizing the efficient use of natural resources while minimizing environmental impacts arising from its operations. This is achieved through the adoption of energy-efficient and environmentally friendly technologies.
The Group has established measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, while fostering innovation to enhance operational processes. Furthermore, affiliated companies are encouraged to implement greenhouse gas reduction measures and energy management practices in alignment with industry regulations. A dedicated unit is responsible for monitoring performance to ensure effective management of both direct and indirect greenhouse gas emissions.
Thoresen Thai Agencies: TTA
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change Management Approach
TTA is committed to sustainable business operations and supports global efforts to limit the rise in average global temperature to no more than 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. This commitment is reflected in various initiatives, such as improving energy efficiency, reducing electricity consumption, and transitioning TTA from fuel-powered to electric vehicles. Furthermore, stakeholders and all relevant sectors are encouraged to contribute to achieving climate change goals.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change Management Activities and Climate Change Initiatives
Transitioning TTA’s from Fuel-Powered to Electric Vehicles
In alignment with the commitment to reducing environmental pollution, TTA has undertaken the transition from fuel-powered to electric vehicles. This initiative reflects the dedication to contributing to air pollution reduction and promoting sustainable transportation solutions.
Performance in 2024
Remark /1 Considering the following categories: (3) Fuel- and energy-related activities, (6) Business travel, and (7) Employee commuting (CO2 emissions from employee commuting are calculated based on 41.26 percent of total employees) amounting to 499, 5,053, and 46 metric tCO₂ equivalent, respectively.2024 Scope 1 Scope 2 Scope 3/1 Total 3 Scopes CO2 Emissions (tCO2 equivalent) of TTA 51 490 5,598 6,139 Mangrove Reforestation Project for Ecosystem and Environmental Sustainability
To operationalize a mission to “give back to the society and environment to lead towards sustainable development”, TTA’s subsidiary V Ventures Technologies Co., Ltd. (VVT) takes participation in the mangrove reforestation project in Klaeng District, Rayong Province, Thailand. Extending to approximately 740 rai, this mangrove cover is estimated to reduce/store greenhouse gases (GHGs) by 34,785 tCO₂ equivalent over a span of 5 years, equivalent to preserving as many as over 500,000 trees.
The project site has undergone rehabilitation to facilitate planting, with mangroves properly maintained and handled by the Department of Marine and Coastal Resources—both project owner and primary developer—in partnership with Siam TC Technology Company Limited—subsidiary under Ditto (Thailand) Public Company Limited Group—through relevant documents of rights.
In light of mangrove forests’ pivotal role in absorbing carbon dioxide and, in turn, sequester GHG emissions into the atmosphere, the project was successfully classified as “reduction, absorption, and removal of greenhouse gases from the forestry and agriculture sectors” project type under the Thailand Voluntary Emission Reduction Program (Standard T-VER) in mid-2024.

In addition, the coastal ecosystem stores carbon in the form of biomass and belowground sediments through deposition, advances ecosystem sustainability, provides shelter for endangered species, contributes to local livelihoods, and serves as a defense and buffer against natural disasters, including reducing the impact of waves on shore and coastal erosion. The coastal ecosystem also promotes local fisheries and well-being of nearby communities, maintaining holistic ecological balance that favors lives in the neighborhoods.
In pursuit of carbon credit verification and certification within the next 5 years, the project would further TTA’s commitment to social and environmental responsibility as well as a force that propels Thailand to fulfill its intent to reduce GHG emissions as pledged on a global stage and to better integrate environmental sustainability nationwide.
Green Win Bangkok (Motorcycle Taxi) Project: Tackling PM 2.5 Pollution
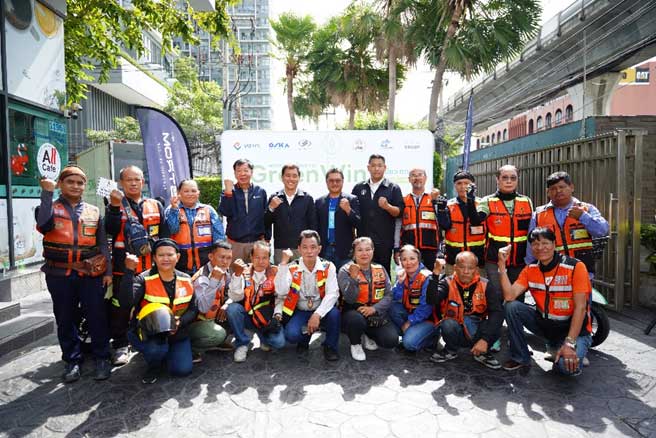

TTA, in collaboration with Strom (Thailand) Co., Ltd., the Bangkok Metropolitan Administration, VST ECS (Thailand) Co., Ltd., Oscar Holding Co., Ltd., Easy Transporter (Thailand) Co., Ltd., and the Motorcycle Taxi Association of Thailand, has launched the "Green Win Bangkok Project". This initiative promotes the adoption of electric motorcycles in Bangkok to reduce pollution and enhance the quality of life for motorcycle taxi drivers, particularly addressing the critical issue of PM2.5 air pollution in Bangkok and its surrounding areas.
Guided by the principle that "Every Mile You Ride Shapes the Future of Planet," the project successfully deployed 1,081 electric motorcycles in 2024. This has resulted in a reduction of 3,065,265 kgCO2—an impact equivalent to planting 340,585 trees.
Thoresen Shipping: TSS
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Management Approach
The company closely monitors environmental regulations and compliance requirements, setting CO2 emission reduction targets in line with IMO standards continuously every year. A dedicated team of experts prepares action plans to ensure alignment with these regulations. The company has set a goal to reduce CO2 emissions by 2 percent in 2025. The focus is on optimizing operations to benefit stakeholders, customers, and the environment, with a strong emphasis on environmental factors.
Furthermore, the company remains committed to enhancing and upgrading ship engines and managing the fleet in an environmentally friendly manner, aiming to continually reduce CO2 emissions to exceed applicable standards. The company is also developing plans to study the feasibility of maintaining CO2 emissions within IMO limits, particularly in relation to the Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI) and Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII), to control air pollution. These efforts are conducted in close collaboration with relevant authorities, and the company ensures proper maintenance plans for engine upkeep and waste disposal systems.
Additionally, the company promotes environmental awareness among crew members, encouraging them to recognize the importance of environmental sustainability. Initiatives such as waste segregation on ships and reducing plastic usage onboard are part of these efforts. By prioritizing environmental responsibility, the company enhances its credibility with stakeholders and maintains a positive public image. This commitment to sustainability also provides a competitive advantage, as various agencies now prioritize partnering with organizations that focus on environmental concerns.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change Management Activities and Initiatives
The company's fleet has implemented technical improvements to reduce CO2 emissions, ensuring the emissions are in line with engine capacity and ship speed. Currently, the entire fleet of Thoresen Shipping complies with the EEXI standard. Out of the 24 ships in the fleet, 8 are capable of operating at their maximum speed according to their specifications, while the remaining 16 operate at speeds in accordance with the designated EPL (Engine Power Limitation). In terms of the CII, Thoresen Shipping's fleet has achieved a ranking that meets the required standards, which is classified within the A – C range.
Installation of Engine Speed Reduction Devices
As CO2 emissions from ship engines are a major contributor to greenhouse gases, the company has installed engine speed reduction devices to decrease fuel consumption. These modifications help reduce fuel burn while ensuring safety during operations. The modifications consider the optimal speed and ensure the fleet's ability to meet customer demands effectively and efficiently.
Performance in 2024
In 2024, the company experienced an increase in CO2 emissions, 303,009 tCO2 equivalent in 2023 to 335,685 tCO2 equivalent, which represents an 11 percent increase. This rise was due to longer shipping routes, primarily a result of the conflict in the Red Sea. As a result, fuel consumption increased, leading to a higher volume of CO2 emissions in 2024.
Nevertheless, Thoresen Shipping remains committed to maintaining its standards and enhancing the technical performance of its fleet to provide the highest level of service and efficiency to customers. Additionally, the Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII) of the Thoresen Shipping fleet has been certified by a globally recognized standard organization (Ship Classification: Bureau Veritas), with the average CII of the fleet being consistent with industry expectations.
Greenhouse Gas Scope 1 2022 2023 2024 Number of Ships 24 24 24 CO2 Emissions (tCO2 equivalent) 340,487 303,009 335,685 Average CO2 Emission Intensity for Cargo Transportation (CII: grams/tone-mile) 4.98 4.47 5.16 PH Capital: PHC
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Management Approach
PH Capital is acutely aware of the challenges posed by global warming, an issue receiving increasing attention from consumers. As a key player in the food service industry, PHC is committed to supporting and promoting the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. The company's operations have identified significant emissions sources: refrigerants used in air conditioners and refrigerators for ingredient storage, and electricity consumption for food preparation and facility equipment across its outlets. The primary strategy for reducing these emissions and conserving energy is the careful selection and use of energy-efficient operational equipment. Consequently, the company mandates the use of air conditioners that minimize greenhouse gas emissions in its Pizza Hut outlets. For new store openings, air conditioning systems that utilize R32 refrigerant will be prioritized for those employing refrigerant-based systems. Furthermore, PHC is collaborating with Daikin Industries (Thailand) Co., Ltd. to assess and optimize refrigeration systems in its stores, focusing on energy efficiency, effective layout planning, and proper operation to further reduce emissions. Therefore, the company believes that the essential first step in reducing greenhouse gas emissions is selecting and using the most energy-efficient equipment available.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change Management Activities and Initiatives
Selection of Air Conditioners that Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions
In 2024, the company installed 62 inverter air conditioners, totaling 2,424,000 BTU, which helped reduce CO2 emissions by 79,357 tCO2 equivalent per year.
Performance in 2024
2024 Scope 1 Scope 2 Scope 3 Total 3 Scopes CO2 Emissions
(tCO2 equivalent)- 15,783 - 15,783 Mermaid Maritime: MML
The 2024 Greenhouse Gas Emissions data for MML reflects significant changes driven by operational expansion and a new business model. This year marks the inclusion of Scope 3 emissions, introducing emissions from of third party chartered vessels into the sustainability report. This step aligns with GRI (305-1a) reporting standards and underscores MML's commitment to a comprehensive approach to sustainability reporting, as guided by SDG Goal 13: Climate Action and the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations.
Data was collected for 14 of third Party vessels deemed material, supporting projects with Chevron Thailand Exploration and Production Co., Ltd. (Chevron) and PTT Exploration and Production Public Company Limited (PTTEP). Data gaps for the remaining 16 of third Party vessels present an opportunity for improved reporting.
Including Scope 3 emphasizes MML’s commitment to addressing its indirect carbon footprint, aligning with SDG Goal 13: Climate Action.
Greenhouse Gas Scope 1-Fuel Consumption (305-1a) 2023 2024 2025 Target Fuel Consumption (tons) 7,361 13,113 12,577 CO2 Intensity = 86 (5 percent reduction) CO2 equivalent (tons) 34,671 35,405 33,958 Annual Revenue
(US$ 000,000)224 274 375 CO2 Intensity (tons/US$) 155 129 91 GHG Scope 3 Fuel Consumption (305-1a) 2022 2023 2024 Fuel Consumption (tons) - - 33,127 CO2 equivalent (tons) - - 89,443 Annual Revenue
(US$ 000,000)224 274 138 CO2 Intensity (tons/US$) - - 643 Key Emissions Data
Scope 1 (Owned and operationally controlled vessels):
- Fuel Consumption: 12,577 tons, a 4.1 percent reduction from 13,113 tons in 2023
- CO2 equivalent Emissions: 33,958 tons, reflecting a 4.1 percent decrease from 35,405 tons in 2023
- CO2 Intensity: 91 tons/US$, showing a 29.5 percent improvement compared to 129 tons/US$ in 2023
Scope 3 (Third party vessels):
- Fuel Consumption: 33,127 tons, a newly introduced category in 2024, covering emissions from major projects
- CO2 equivalent Emissions: 89,443 tons, emphasizing the impact of 3rd party vessel operations
- CO2 Intensity: 643 tons/US$, set as a potential baseline for future reporting
Combined Emissions:
- Total CO2 equivalent Emissions: 123,401 tons, a 248.3 percent increase from 35,405 tons in 2023, driven by the inclusion of Scope 3
Operational Expansion:
MML’s expanded operations in 2024 necessitated the use of 30 3rd party vessels to support Chevron and PTTEP projects, reflecting a shift in its business model. 3rd party vessels, often lacking advanced greenhouse gas emission control technologies may have contributed to the increased CO2 emissions and intensity. Regulatory industry standard requirements and operational constraints for vessels may have further contributed to increased greenhouse gas emissions.
Opportunities for Improvement:
- Data Collection and Monitoring: Enhance systems to capture comprehensive data from all 3rd party chartered vessels
- Fuel Efficiency Initiatives: Adopt operational practices to optimize routing, reduce idling, and maximize fuel efficiency across all vessels
- Client Collaboration: Engage clients in co-developing strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions 3. across the supply chain
Air Quality Calculations
MML is committed to advancing its air quality management initiatives by aligning with GRI 305-1a standards, reflecting a strong dedication to minimizing emissions and mitigating environmental impacts. The 2024 Air Quality Management data underscores the company's proactive efforts to reduce SOx (Sulfur Oxides) and NOx (Nitrogen Oxides) emissions, critical pollutants affecting marine environments.
By addressing emissions from both owned and operationally controlled vessels (Scope 1) and 3rd party vessels (Scope 3), MML demonstrates a comprehensive approach to air quality improvement. The company’s data is verified by DNV, ensuring transparency and accuracy in its sustainability reporting.
Scope 1-NOx and SOx(305-1a) 2022 2023 20224 Target SOx Emissions (tons) N/A 524 503 SOx Intensity = 1.2 (5 percent reduction) Annual Revenue
(US$ 000,000)224 274 375 SOx Emission Intensity
(tons/US$ 000,000)N/A 1.9 1.3 NOx Emissions (tons) N/A 1,169 1,121 NOx Intensity = 2.9
(5 percent reduction)NOx Emission Intensity
(tons/ US$ 000,000)N/A 4.2 3 Scope 3-NOx and SOx(305-1a) 2022 2023 2024 SOx Emissions (tons) - - 1,325 Annual Revenue
(US$ 000,000)224 274 138 SOx Emission Intensity
(tons/US$ 000,000)- - 10 NOx Emissions (tons) - - 2,953 NOx Emission Intensity
(tons/ US$ 000,000)- - 21 Key Air Quality Data
Scope 1 (Owned and operationally controlled vessels):
- SOx Emissions: Reduced to 503 tons in 2024 from 524 tons in 2023, reflecting a 4 percent reduction
- NOx Emissions: Reduced to 1,121 tons in 2024 from 1,169 tons in 2023, achieving a 4.1 percent reduction
- SOx Emission Intensity: Decreased to 1.3 tons/US$ 000,000 in 2024, a 31.6 percent reduction from 1.9 tons/US$ 000,000 in 2023
- NOx Emission Intensity: Improved to 3 tons/US$ 000,000 in 2024, a 28.6 percent reduction from 4.2 tons/US$ 000,000 in 2023
Scope 3 (Third party vessels):
- SOx Emissions: Newly reported in 2024, totalling 1,325 tons from third party vessels
- NOx Emissions: Recorded at 2,953 tons, reflecting emissions from 14 third party vessels
- SOx Emission Intensity: Recorded at 10 tons/US$ 000,000, set as a potential baseline for future reporting
- NOx Emission Intensity: Recorded at 21 tons/US$ 000,000, also established as a potential baseline
Combined Data:
- Annual Revenue: Increased to US$ 513 million in 2024, up from US$ 274 million in 2023, reflecting an 87.6 percent increase
- Emission Intensity Progress: Significant strides were made in reducing Scope 1 emission intensities, with the inclusion of Scope 3 emissions providing a broader understanding of operational impacts
Opportunities for Improvement:
- Install exhaust scrubbers: Collaborate with key stakeholders to assess retrofitting costs and develop co-funding models for installing emission control technologies on aging vessels
- Conduct training for vessel operators on emission reduction practices: Organize workshops focusing on fuel-efficient navigation, maintenance best practices, and the environmental impact of emissions
- Advocate for cleaner fuel for all vessels: Introduce pilot programs for the use of biofuels and assess feasibility for broader adoption in all vessels
-
Waste Management
-
Waste Management(3-3, 306-1, 306-2)
Due to diverse operations of the Group, various types of waste are generated, including office waste, industrial wastewater, ballast water, food preparation waste, plastic waste, chemicals, and other waste materials. Because these wastes differ in type and required management methods, a systematic waste management approach that meets legal requirements is essential to prevent legal violations and mitigate potential environmental and health impacts on surrounding communities. Furthermore, the Group aims to minimize the risk of increased disposal costs.
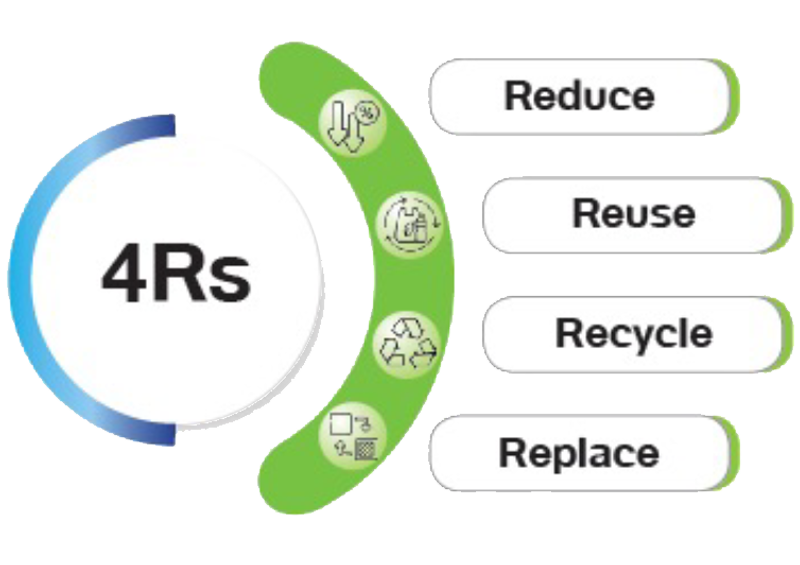
The Group places significant emphasis on waste management and focuses on efficient resource use. It has established guidelines aligned with the organization's environmental policy, aiming to manage waste effectively and maximize the utility of resources across the entire value chain. Continuous efforts are made to minimize waste generation. The Group supports and encourages both employees and subsidiaries to manage waste within the organization according to the principles of a circular economy, adhering to the 4Rs: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, and Replace.
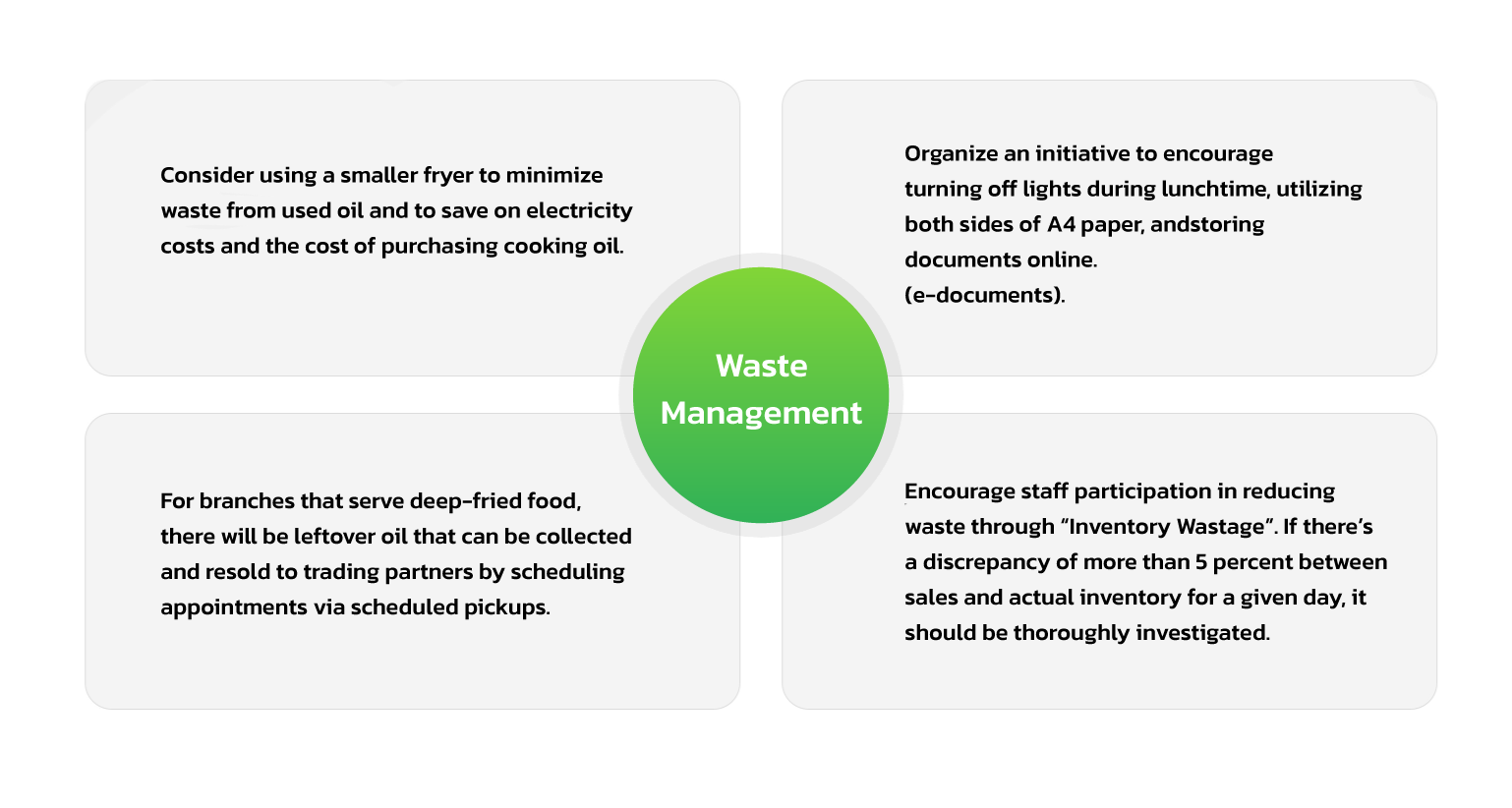
- Reduce (resource consumption and waste generation)
- Reuse (materials to extend their lifecycle)
- Recycle (waste into new, usable materials)
- Replace (with sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives)
TTA has established a comprehensive waste management monitoring system covering waste segregation, storage, transportation, and disposal, while also tracking waste volume and disposal methods. To promote resource efficiency and a culture of responsible waste management, TTA conducts training, awareness campaigns, and posts informational notices in office spaces and on waste bins. TTA believes these initiatives will optimize resource utilization, reduce waste management costs, and enable the resale or repurposing of sorted waste materials, such as used cardboard boxes, paper, and oil, generating additional revenue and enhancing reputation for sustainable corporate management in the long term.
Waste Management Policy
The Group has established a waste management policy as part of TTA's Environmental Policy, emphasizing the efficient use of natural resources and proper waste management. This policy incorporates the 4Rs principles—Reduce (minimizing usage), Reuse (utilizing items multiple times), Recycle (reprocessing materials), and Replace (substituting with more sustainable alternatives)—to ensure sustainable business operations.
Thoresen Thai Agencies: TTA
Waste Management Approach
TTA aims to reduce non-hazardous waste and non-hazardous residues by 2 percent annually. In 2023, the Company continued initiatives to minimize waste generation, focusing on employee awareness and promoting responsible paper usage (for example, reducing single-sided printing). Various measures were implemented, including e-learning materials, online assessments, and regular communication. However, in 2024, TTA's non-hazardous waste and residues increased to 1,805 kilograms, a 19.5 percent rise from the previous year, primarily due to business expansion and structural adjustments that diversified investments and increased the workforce. Despite not fully achieving the reduction target, TTA remains committed to waste minimization initiatives and sustainable resource management.
Performance
2022 2023 2024 Amount (Baht) 56,230 51,475 61,531 ↑ 19.5 percent Volume of Non-Hazardous Waste and Residues Orders (kg) 1,564 1,510 1,805 ↑ 19.5 percent Waste Management Activities and Initiatives
Corporate Waste Management at the Source
TTA implements waste segregation based on the 4Rs principles (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, and Replace) to maximize resource efficiency and minimize waste generation. This involves reducing usage, reusing materials, recycling waste, and replacing non-sustainable resources with more environmentally friendly alternatives. The initiative aims to decrease office waste through a structured segregation system, with designated waste bins installed across various locations to facilitate proper recycling and storage.
In 2024, TTA began weighing segregated waste, recording a total of 4,521 kilograms of non-hazardous waste and residues. To further reduce waste, the Company actively promoted awareness among employees, encouraging them to minimize waste generation as part of an initial step toward a zero-waste lifestyle. Employees are urged to adopt simple habits that help reduce environmental impact, such as:
- Carrying a reusable water bottle: Bringing a personal water bottle everywhere promotes hydration while significantly reducing plastic bottle consumption
- Using personal shopping bags: Declining plastic bags and opting for reusable shopping bags when making purchases, whether for household goods or daily essentials
- Switching to electronic documents: Opting out of paper-based mails, bills, and flyers
- Choosing biodegradable trash bags: Ensuring trash bags are labeled as 100 percent biodegradable, as some products may only be partially degradable
Plastic Bottle-to-Robe Recycling Project
TTA has continued the TTA Zero Waste Project for the 4th consecutive year to raise employee awareness of proper waste management. In 2024, TTA donated 4,425 used PET plastic bottles, weighing 199.3 kilograms, collected from employee contributions to Wat Chak Daeng in Samut Prakan Province. These bottles were recycled into saffron robes for Buddhist monks (1 robe = 60 bottles). This initiative contributed to a CO2 reduction of 0.42 tCO2 equivalent.

Thais Say No to E-Waste
TTA has partnered on the "Thais Say No to E-Waste" initiative to properly manage electronic waste (E-Waste). In 2023, TTA began efforts to raise awareness of the issues and impacts of electronic waste by creating informational materials and setting up collection points for E-Waste. Employees were encouraged to dispose of both personal and office electronic waste in the designated E-Waste bins, which would be properly recycled with no leftover waste and zero e-waste sent to landfills. This initiative marks a positive start in promoting awareness and proper electronic waste management at both the organizational and national levels.
In 2024, TTA encouraged employees to continue disposing of electronic waste, with a total of 532 items collected, weighing 64 kilograms. This contributed to a CO2 reduction of 287.28 kgCO2, equivalent to planting 32 trees.

Mahaheng Desk Organization Initiative
Organizing the workspace is crucial, as it is where office employees spend the majority of their time. Arranging desks according to ergonomic principles and based on individual needs increases convenience, improves focus, and enhances work efficiency. TTA organized this initiative, encouraging employees to take "before" and "after" photos of their desks over the course of 1 week. The goal was to foster good habits in maintaining cleanliness and organizing items in an orderly and systematic manner.
Example of Employee Desk Organization


Mangrove Plantation Project
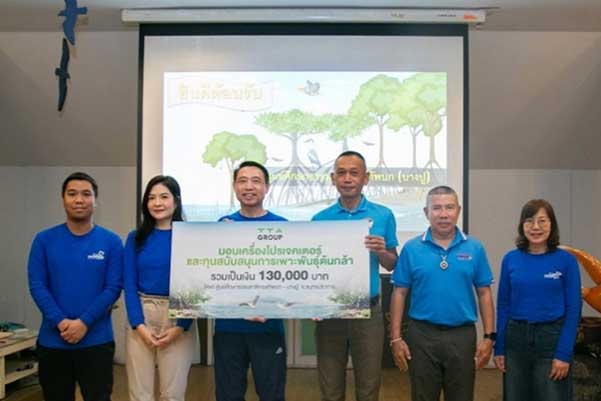
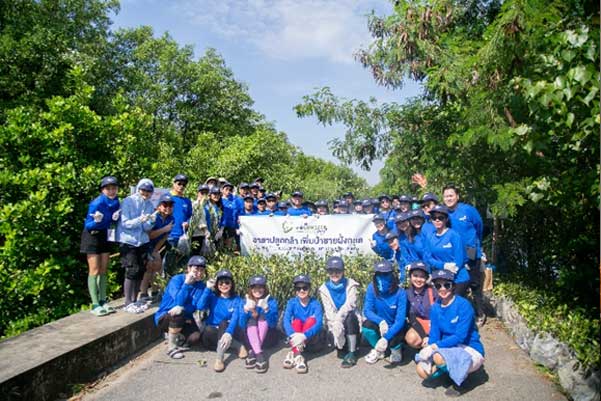
A total of 60 executives and volunteer employees participated in the activity "TTA Volunteer Spirit: Planting Seedlings to Increase Coastal Mangrove Forests" at the Army Natural Study Center in Bang Pu, Samut Prakan Province. The initiative supported the planting of 1,500 mangrove saplings and the donation of a projector for the learning center. The projector will be used to train visitors on the proper guidelines for mangrove ecosystem restoration and conservation.


Thoresen Shipping: TSS
Waste Management Approach
Thoresen Shipping continues to operate in alignment with its policies and has set targets for waste management, adhering to international regulations. This is to ensure that there is no negative impact on marine ecosystems and to cultivate a culture of waste management in line with the 4Rs: Reduce (reducing usage), Reuse (reusing materials), Recycle (recycling materials), and Replace (using alternative materials). These initiatives aim to ensure that the company's operations are both efficient and sustainable. Furthermore, hazardous waste disposal is carried out by certified agencies to guarantee proper destruction and reduce the risk of marine pollution.
PH Capital: PHC
Waste Management Approach
In the food service sector, improper waste management can lead to significant impacts, such as increased landfill waste, depletion of natural resources, greenhouse gas emissions from waste management processes, and negative effects on the quality of life in surrounding communities. It also presents risks to the long-term sustainability of the business. Therefore, the company places great importance on efficient waste management, covering all stages of the value chain, from reducing waste in the production process and using energy and resources efficiently to managing packaging and waste disposal. The company also promotes collaboration with stakeholders to balance the reduction of negative impacts, cost control, and the long-term sustainability of the organization.
In 2024, the company established guidelines for waste management operations and implemented waste management processes through municipal areas and shopping centers where its branches are located.
Beyond these operations, PHC has systematically integrated the 4Rs principles within the organization to enhance resource management and reduce environmental impact. The guidelines are as follows:
- Reduce: Minimize waste generation through optimized purchase planning and implement the FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory management system to rotate stock, reducing the risk of spoilage or expiration
- Repair: Reduce repair costs by training employees (Handyman) to perform basic repairs themselves
- Refuse: Encourage adherence to established company policies, such as avoiding the use of containers that are harmful to health and choosing environmentally friendly packaging, e.g., paper boxes instead of foam boxes
- Reuse: Effectively reuse materials, e.g. utilize both sides of A4 paper
Pizza Dough Improvement Project to Reduce Food Waste
The company has modified its pizza dough preparation method, extending shelf life from 8 hours to 24 hours. This has resulted in a threefold reduction in discarded expired dough. Additionally, the company has introduced a new type of frozen dough, "SFO Dough," with a shelf life of 4 months, for making Neapolitan pizzas.
Mermaid Maritime: MML
MML complies with MARPOL Annex V, ensuring proper onboard waste segregation and disposal, and adheres to ISO 14001 standards, showcasing strong environmental management practices. Waste management processes are documented, audited, and aligned with sustainability goals, promoting transparency in reporting. Hazardous waste handling is conducted in partnership with WMS Thailand, a certified waste management provider, ensuring compliance with legal and environmental standards.
Waste Generation 2023 2024 2025 Hazardous Waste Generation (tons) 95 47 863 Non-Hazardous Waste Generation (tons) 1,362 681 1,194 Total Waste Generation (tons) 1,458 728 2,057 Hazardous Waste
Key Waste Types:
- Used Cooking Oil (1.9 metric tons): Discharged to shore contractors via WMS Thailand
- Waste Oil/Sludge (133.63 metric tons): Transported by supply boats to WMS Thailand for disposal
- E-Waste (14.08 metric tons): Compressed into pellets and managed by WMS for landfilling
- Contaminated Wastewater (670.5 metric tons): Processed by blending into fuel for energy recovery
- Used Fluorescent Lamps (2 metric tons): Recycled through WMS Thailand
Disposal Methods:
- WMS Thailand facilitates the recycling, landfilling, or energy recovery of hazardous waste
- Non-recyclable items such as oily rags and soda lime are disposed of offshore under MARPOL regulations
Non-Hazardous Waste
Key Waste Types:
- Plastics (50 metric tons): Recycled through authorized facilities
- Food Waste (151.5 metric tons): Disposed of as per MARPOL requirements
- Household Waste (508.8 metric tons): Transferred to WMS Thailand for proper handling
- Metal Scrap (67.3 metric tons): Recycled or landfilled
- Used Packaging (116.1 metric tons): Recycled via WMS Thailand's supply chain partners
Recycling Initiatives:
- Paper and Wood Waste (100.5 metric tons): Recycled, reflecting resource conservation efforts
Waste Segregation and Disposal Practices
Ship-Generated Waste:
- Segregated into solid and liquid categories
- Managed in compliance with MARPOL requirements, either disposed of at sea or transferred to WMS Thailand for authorized handling
Onshore Waste:
- Hazardous waste like plastics and fluorescent lamps is recycled through WMS Thailand-certified facilities
- Non-hazardous waste such as old furniture is donated to orphanages or sold to employees, with remaining items sent to municipal landfills
Mermaid Subsea Services (Thailand) Ltd (MSST) Paper Usage Details(305-1a)
2023 2024 Target Paper Used (Quires) 83 93 84
(10 percent reduction)Paper Usage and Environmental Impact
MSST recorded an increase in paper usage from 83 quires in 2023 to 93 quires in 2024, indicating a rise of approximately 12 percent year-on-year. To address this, MSST has set a sustainability target to achieve a 10 percent reduction in paper usage by 2025, aligned with the principles of GRI (305-1a), focusing on reducing carbon emissions and environmental impact.
Environmental Impact of Paper Usage
Paper production contributes significantly to deforestation, water consumption, and energy use, resulting in greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, improper disposal of paper waste leads to methane emissions during decomposition. By reducing paper usage, MSST aims to reduce its carbon footprint and promote resource efficiency.
Measures to Reduce Paper Usage
To fulfill the sustainability goals, MSST is implementing the following initiatives:
- Digital Transformation: Transitioning to digital documentation to reduce paper dependency
- Employee Awareness Campaigns: Promoting a "think before you print" culture
- Paper Recycling: Ensuring used paper is collected and recycled appropriately
- Procurement of eco-friendly paper
- Sourcing paper with high recycled content and low-carbon production methods
PM Thoresen Asia Holdings: PMTA
Waste Management Approach
In PMTA's agricultural chemical business operations, licensed contractors are hired for waste collection, transportation, treatment, and disposal to manage both hazardous and non-hazardous waste generated from business operations in Vietnam, in compliance with Vietnamese laws and regulations.
- Phu My Xanh Environment Investment Joint Stock Company is responsible for collecting and transporting household waste to legally authorized treatment facilities
- Ka Loc Company is responsible for collecting, transporting, treating, and disposing of general and hazardous waste

PMTA requires waste segregation according to various regulations and ensures appropriate waste transportation. Additionally, the company has implemented wastewater treatment systems and air pollution control measures, aiming to prevent pollution from wastewater treatment or maximize treatment effectiveness. Since 2019, PMTA has implemented a project to reuse used rubber as fuel, which helps reduce the company's fuel purchase costs and decrease sulfur gas emissions that impact the environment. However, PMTA places high importance on waste management and regularly conducts inspections, monitors, and reports on waste management to government authorities.
Performance
Type of Waste Waste Volume (kilograms) 2022 2023 2024 Total Non-Hazardous Waste 99,078 88,662 95,638 Total Hazardous Waste 20,682 14,988 22,090